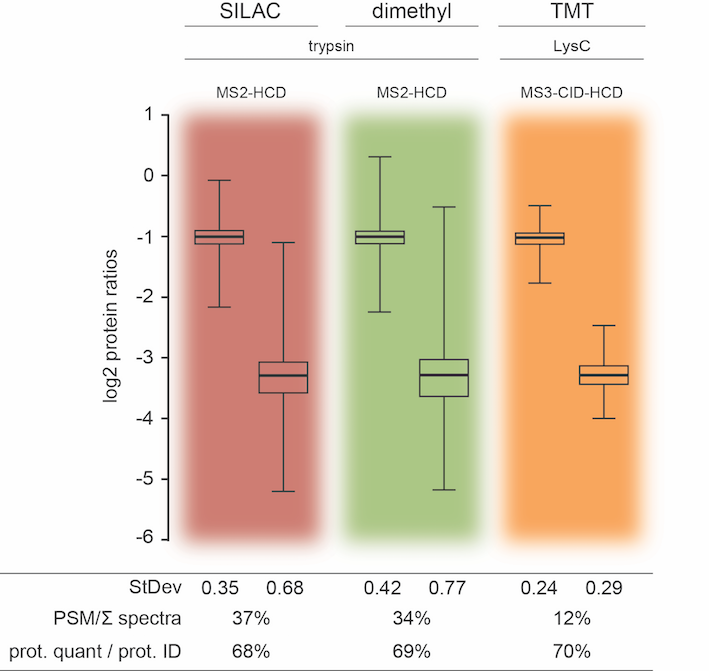
Several quantitative mass spectrometry based technologies have recently evolved to interrogate the complexity, interconnectivity and dynamic nature of proteomes. Currently, the most popular methods use either metabolic or chemical isotope labeling with MS based quantification or chemical labeling using isobaric tags with MS/MS based quantification. Here, we assess the performance of three of the most popular approaches through systematic independent large scale quantitative proteomics experiments, comparing SILAC, dimethyl and TMT labeling strategies. Although all three methods have their strengths and weaknesses, our data indicate that all three can reach a similar depth in number of identified proteins using a classical (MS2 based) shotgun approach. TMT quantification using only MS2 is heavily affected by co-isolation leading to compromised precision and accuracy. This issue may be partly resolved by using an MS3 based acquisition; however, at the cost of a significant reduction in number of proteins quantified. Interestingly, SILAC and chemical labeling with MS based quantification produce almost indistinguishable results, independent of which database search algorithm used.
Altelaar AF, Frese CK, Preisinger C, Hennrich ML, Schram AW, Timmers HT, Heck AJ, Mohammed S.
J Proteomics. 2013 Aug 2;88:14-26.